Cetirizine Synthesis Pdf
Synthesis of Cetrizine using Chlorobenzhydryl chloride. Cetirizine Synthesis. Download as PDF or read online from Scribd.

System Maintenance: From Saturday, 10 February, 5:00PM EST – Sunday, 11 February, 1:00AM EST Please be aware that pubs.acs.org is undergoing maintenance that will have an impact on applications that require a login or ACS ID, including the Registration and MyAccount functions. Individual users will not be able to log-in to access their subscribed content; purchase single articles; access ACS ChemWorx, or change their e-Alert subscriptions. We appreciate your patience as we make improvements to the ACS Publications platform.
Contents. Medical uses Allergies Cetirizine's primary indication is for and other allergies. Because the symptoms of itching and redness in these conditions are caused by histamine acting on the H 1 receptor, blocking those receptors temporarily relieves those symptoms. Renewable energy program office. Cetirizine is also commonly prescribed to treat acute and (in particular cases) chronic, more efficiently than any other second-generation antihistamine. Rhinovirus infection and have been shown to be elevated in acute respiratory distress syndrome. One recent study of airway epithelial cells showed that, the active of cetirizine, may have beneficial effects on the pathophysiologic changes related to human rhinovirus infection. Kimura's disease Cetirizine is an effective agent in treating the symptoms of which predominantly affects the lymph nodes and soft tissue of the head and neck in the form of tumor-like lesions.
Cetirizine's properties of being effective both in the treatment of (itching) and as an anti-inflammatory agent make it suitable for the treatment of the pruritus associated with these lesions. In a 2005 study, the American College of Rheumatology conducted treatments initially using, followed by steroid dosages and, and and supplements over the course of two years. The skin condition of the patient began to improve and the skin lesions lessened.
However, there were symptoms of and observed before the patient was removed from the courses of steroids and placed on 10 mg/day of cetirizine to prevent skin lesions; an agent suitable for the treatment of pruritus associated with such lesions. Asymptomatically, the patient's skin lesions disappeared after treatment with cetirizine, blood counts became normal, corticosteroid effects were resolved, and a remission began within a period of two months. It is also thought that the inhibition of eosinophils may be the key to treatment of Kimura's disease due to the role of eosinophils, rather than other cells with regards to the lesions of the skin. Available forms Cetirizine is available in the form of 5 and 10 mg. Adverse effects Commonly reported side effects of cetirizine include (16%), (5.7%), (5–20%), and (5.6%), while more serious but rare side effects include, and. Withdrawal Long-term daily usage of cetirizine may result in what resembles antihistamine dependency.
No official study has been conducted to determine how long a patient may take cetirizine daily before expecting to encounter withdrawal symptoms when treatment stops. Many patients seeking help with withdrawal symptoms report having taken cetirizine for more than three years, while others report having taken it for no longer than one week. Insatiable, generalized itching is the most commonly-reported withdrawal side effect, though others have reported severe of original, pre-treatment systems as well, including sneezing and runny nose. Pharmacology. L-Stereoisomer, (top) and D-stereoisomer of cetirizine. Pharmacodynamics Cetirizine acts as a highly of the. The K i values for the H 1 receptor are approximately 6 nM for cetirizine, 3 nM for, and 100 nM for dextrocetirizine, indicating that the is the main active form.
Cetirizine has 600-fold or greater for the H 1 receptor over a wide variety of other sites, including, and among many others. The drug shows 20,000-fold or greater selectivity for the H 1 receptor over the five muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, and hence does not exhibit effects. It shows negligible inhibition of the channel ( 30 µM) and no has been observed with cetirizine at doses of up to 60 mg/day, six times the normal recommended dose and the highest dose of cetirizine that has been studied in healthy subjects. Cetirizine crosses the only slightly, and for this reason, it produces minimal sedation compared to many other antihistamines. A (PET) study found that brain occupancy of the H 1 receptor was 12.6% for 10 mg cetirizine, 25.2% for 20 mg cetirizine, and 67.6% for 30 mg hydroxyzine. (A 10 mg dose of cetirizine equals about a 30 mg dose of hydroxyzine in terms of peripheral antihistamine effect.) PET studies with antihistamines have found that brain H 1 receptor occupancy of more than 50% is associated with a high prevalence of somnolence and cognitive decline, whereas brain H 1 receptor occupancy of less than 20% is considered to be non-sedative. In accordance, H 1 receptor occupancy correlated well with subjective sleepiness for 30 mg hydroxyzine but there was no correlation for 10 or 20 mg cetirizine.
As such, brain penetration and brain H 1 receptor occupancy by cetirizine are dose-dependent, and in accordance, while cetirizine at doses of 5 to 10 mg have been reported to be non-sedating or mildly sedating, a higher dose of 20 mg has been found to induce significant in other studies. Cetirizine has been shown to inhibit and release. At a dosage of 20 mg, Boone et al. Found that it inhibited the expression of in patients with. Pharmacokinetics Absorption Cetirizine is rapidly and extensively upon in tablet or syrup form. The of cetirizine is at least 70% and of levocetirizine is at least 85%.
The of cetirizine is approximately 1.0 hour regardless of formulation and its has been reported to be as early as 20 minutes. The of cetirizine have been found to increase linearly with dose across a range of 5 to 60 mg. Its following a single dose has been found to be 257 ng/mL for 10 mg and 580 ng/mL for 20 mg. Food has no effect on the of cetirizine but has been found to delay the T max by 1.7 hours (i.e., to approximately 2.7 hours) and to decrease the C max by 23%. Similar findings were reported for levocetirizine, which had its T max delayed by 1.25 hours and its C max decreased by about 36% when administered with a high-fat meal.
Of cetirizine occur within 3 days and there is no accumulation of the drug with chronic administration. Following once-daily administration of 10 mg cetirizine for 10 days, the mean C max was 311 ng/mL. Distribution The mean of cetirizine has been found to be 93 to 96% across a range of 25 to 1,000 ng/mL independent of concentration. Plasma protein binding of 88 to 96% has also been reported across multiple studies. The drug is bound to with high, while and contribute much less to total plasma protein binding.
The unbound or free fraction of levocetirizine has been reported to be 8%. The true of cetirizine is unknown but is estimated to be 0.3 to 0.45 L/kg. Cetirizine poorly and slowly crosses the, which is due mainly to its chemical properties but also to a minor extent to its activity as a. Metabolism Cetirizine does not undergo extensive. It is notably not metabolized by the system.
Because of this, it does not interact significantly with drugs that or cytochrome P450 enzymes such as,. While cetirizine does not undergo extensive metabolism or metabolism by the cytochrome P450 enzyme, it does undergo some metabolism by other means, the of which include and. Plasma radioactivity attributed to unchanged cetirizine is more than 90% at 2 hours, 80% at 10 hours, and 70% at 24 hours, indicating limited and slow metabolism. The enzymes responsible for of cetirizine have not been identified. Elimination Cetirizine is approximately 70 to 85% in the and 10 to 13% in the.
About 50 or 60% of cetirizine eliminated in the urine is unchanged. It is eliminated in the urine via an mechanism. The of cetirizine ranges from 6.5 to 10 hours in healthy adults, with a mean across studies of approximately 8.3 hours.
Cetirizine Synthesis
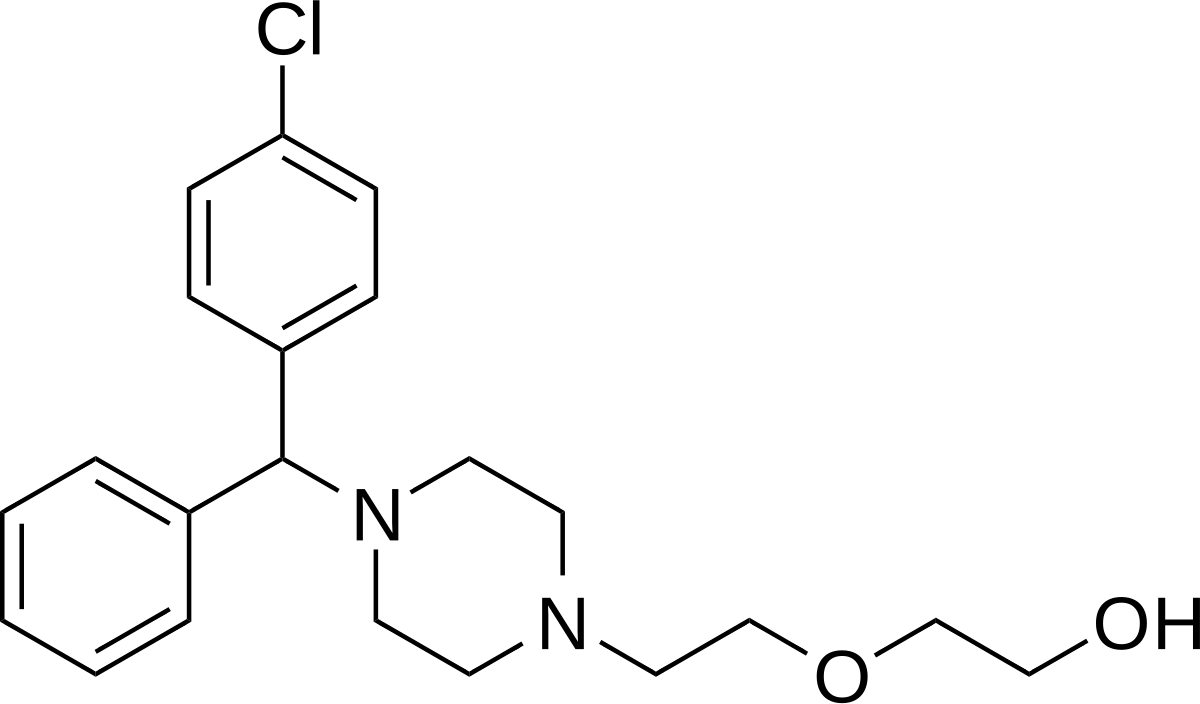
Its is at least 24 hours. The elimination half-life of cetirizine is increased in the elderly (to 12 hours), in (to 14 hours), and in (to 20 hours). Chemistry Cetirizine contains L- and D. Chemically, is the active L- of cetirizine. The drug is a member of the group of antihistamines. Synthesis.
Jozsef Reiter
Brand names Cetirizine is marketed under the brand names Alatrol, Alerid, Alzene, Cetirin, Cetzine, Cezin, Histazine, Humex, Letizen, Reactine, Razene, Rigix, Triz, Zetop, Zirtec, Zirtek, Zodac, Zyllergy, Zynor, Zyrlek, and Zyrtec among others. Availability Formerly prescription-only in many countries, cetirizine is now available without prescription in most countries. In some countries it is available over-the-counter only in packages containing seven or ten 10 mg doses. Like many other antihistamine medications, cetirizine is commonly prescribed in combination with, a. These combinations are often marketed using the same brand name as the cetirizine with a '-D' suffix ( Zyrtec-D, Virlix-D, etc.).